ARTHROSCOPY REPAIR FOR MENISCAL TEARS
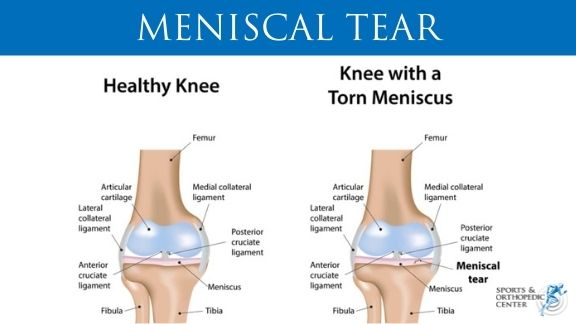
Meniscus tears are among the most common knee injuries. A meniscus is a C-shaped structure that is made out of a strong rubbery material termed fibrocartilage. Each knee has two menisci. These menisci reside between the femur (thigh bone) and the tibia (main bone in lower leg).
The main functions of a meniscus include shock absorption and load transmission. The secondary functions of a meniscus include joint stability, lubrication and nutrition.
SYMPTOMS OF A MENISCAL TEAR
When a meniscus tear initially occurs, a person may hear or feel a “pop” in the knee. The knee often hurts immediately, and it may develop swelling.
 Common symptoms include:
Common symptoms include:
- Pain
- Stiffness
- Swelling
- Knee “catching” or “locking”
- Difficulty straightening the knee fully
- Feeling as if the knee is “giving way”
CAUSES
- Acute meniscus tears often happen during sports. These can occur through either a contact or non-contact injury—for example, a pivoting or cutting injury.
- As people age, they are more likely to have degenerative meniscus tears. Aged, worn tissue is more prone to tears. An awkward twist when getting up from a chair may be enough to cause a tear in an aging meniscus.
TREATMENT
In some cases, you can treat the pain and discomfort of a meniscus tear with RICE therapy:
- Rest
- Ice
- Compression
- Elevation
However, if you suspect you’ve injured your meniscus, you should see a doctor. Many meniscus injuries occur in the inner two-thirds of the meniscus, in the “white” zone where blood supply is not as rich. Without nutrients, these injuries seldom heal on their own.
Left untreated, a damaged meniscus can lead to other problems in your knee. Loose meniscus cartilage may move around inside your joint, leading to locking or popping of the knee and knee instability. A chronically injured meniscus can also lead to arthritis.
SURGICAL OPTIONS FOR MENISCAL TEAR
Arthroscopic excision
This is the most commonly performed treatment option and provides excellent, long term symptom relief for most patients. Although most patients will experience improvement within a few weeks of surgery some may require longer periods due to extensive quadriceps atrophy or other intra-articular pathology.
Arthroscopic repair
In certain, specific cases the meniscus may be able to be repaired. This is usually restricted to those cases where a fresh, peripheral tear is identified at arthroscopy in a young patient. The limited application for meniscal repair is due to the poor blood supply found within most the meniscus meaning only the outer 25% has a viable healing potential. It is an important consideration for many patients that a meniscal repair will necessitate a much-prolonged period of rehabilitation when compared to a simple excision.
If you are still experiencing pain reach out to one of our orthopedic surgeon at Sports & Orthopedic Center for information on how to best manage and monitor your pain.