KNEE REPLACEMENT, ROBOTIC, CUSTOM, PARTIAL, TOTAL
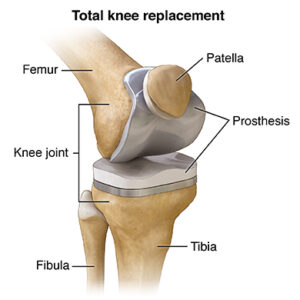
Knee replacement is where portions of the bones that form the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial metal and plastic parts that are used to cap the ends of the bones that form the knee joint, along with the kneecap. It is performed primarily to relieve knee pain and stiffness caused by osteoarthritis.
 There are three common reasons for the procedure:
There are three common reasons for the procedure:
Osteoarthritis: this type of arthritis is age related, caused by the normal wear and tear of the knee joint. It mostly affects patients aged over 50 years, but younger people may have it.
Osteoarthritis is caused by inflammation, breakdown, and the gradual and eventual loss of cartilage in the joints. Over time, the cartilage wears down and the bones rub together. To compensate, the bones often grow thicker, but this results in more friction and more pain.
Rheumatoid arthritis: also called inflammatory arthritis, the membrane around the knee joint to become thick and inflamed. Chronic inflammation damages the cartilage, causing soreness and stiffness.
Post-traumatic arthritis: this type of arthritis is due to a severe knee injury. When the bones around the knee break or the ligaments tear, this will affect the knee cartilage.
TYPES OF KNEE REPLACEMENT
Total knee replacement (TKR): Surgery involves the replacement of both sides of the knee joint. It is the most common procedure.
Surgery lasts between 1 and 3 hours. The individual will have less pain and better mobility, but there will be scar tissue, which can make it difficult to move and bend the knees.
Partial knee replacement (PKR): Partial replacement replaces only one side of the knee joint. Less bone is removed, so the incision is smaller, but it does not last as long as a total replacement.
PKR is suitable for people with damage to only one part of the knee. Post-operative rehabilitation is more straightforward, there is less blood loss and a lower risk of infection and blood clots.
Your doctor can choose from a variety of knee replacement prostheses and surgical techniques, considering your age, weight, activity level, knee size and shape, and overall health.
For most people, knee replacement provides pain relief, improved mobility and a better quality of life. And most knee replacements can be expected to last more than 15 years.
Three to six weeks after surgery, you generally can resume most daily activities, such as shopping and light housekeeping. Driving is also possible at around three weeks if you can bend your knee far enough to sit in a car, if you have enough muscle control to operate the brakes and accelerator, and if you’re not still taking narcotic pain medications.
ROBOTIC SURGERY
In a robotic surgery doctors use a robotic surgical arm to execute parts of the procedure, assisting in areas that demand the steadiest hand and navigating small places. Robotics becomes another tool in the doctor’s kit.
Using CT scans, the robotic arm can work from 3D images of the surgical area and perform a range of tasks, such as:
- Prepare the bone.
- Introduce the implant.
- Balance the implant.
- Check for the right fit.
RECOVERY
With a traditional total knee replacement, the average patient won’t be able to resume normal activities like driving and going to work until 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. Robot-assisted technology could potentially cut this recovery time in half.
Smaller incisions combined with greater surgical precision means that less bone and tissue is disturbed, speeding up the body’s natural healing process.